Topographic Map :
A topographic map is a detailed and accurate illustration of man-made and natural features on the ground such as roads, railways, power transmission lines, contours, elevations, rivers, lakes and geographical names.
The topographic map is a two-dimensional representation of the Earth’s three-dimensional landscape. The most frequently used topographic map is at the scale of 1:50 000.
Topographic maps identify numerous ground features, which can be grouped into the following categories:
Relief: Mountains, valleys, slopes, depressions as defined by contours.
Hydrography : Lakes, rivers, streams, swamps, rapids, falls.
Vegetation: Wooded areas.
Transportation: Roads, trails, railways, bridges, airports/airfield, seaplane anchorages.
Culture: Buildings, urban development, power transmission line, pipelines, towers.
Boundaries: International, provincial/territorial, administrative, recreational, geographical.
Refer to the map legend for a complete listing of all features and their corresponding symbols. Information along the map borders provides valuable details to help you understand and use a topographic map. For example, here you will find the map scale and other important information about the map such as the year, the edition and information pertaining to the map data.
Colours on a Topographical Map :
A variety of colours can be found on a map, each relating to different types of features.
Black shows cultural features such as buildings, railways and power transmission lines. It is also used to show geographical names (toponymy), certain symbols, geographic coordinates and precise elevations.
Blue represents water features, such as lakes, rivers, falls, rapids, swamps and marshes. The names of water bodies and water courses are also shown in blue, as are magnetic declination and UTM grid information.
Green indicates vegetation such as wooded areas, orchards and vineyards.
Contour and its lines
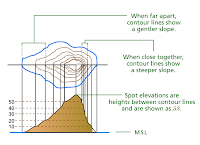
Contour lines connect a series of points of equal elevation and are used to illustrate relief on a map. They show the height of ground above mean sea level (MSL) either in metres or feet, and can be drawn at any desired interval. For example, numerous contour lines that are close to one another indicate hilly or mountainous terrain; when further apart they indicate a gentler slope; and when far apart they indicate flat terrain.
Scale of a Topographical :
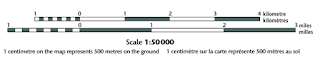
 Maps are made to scale. In each case, the scale represents the ratio of a distance on the map to the actual distance on the ground. A standard topographic map is produced at 1:50 000, where 2 cm on the map represents 1 km on the ground.
Maps are made to scale. In each case, the scale represents the ratio of a distance on the map to the actual distance on the ground. A standard topographic map is produced at 1:50 000, where 2 cm on the map represents 1 km on the ground.Medium-scale maps (e.g. 1:50 000) cover smaller areas in greater detail, whereas small-scale maps (e.g. 1:250 000) cover large areas in less detail. A 1:250 000 scale national topographic system (NTS) map covers the same area as sixteen 1:50 000 scale NTS maps.
Grid on a Topographic Map :
A grid is a regular pattern of parallel lines intersecting at right angles and forming squares; it is used to identify precise positions. To help you locate your position accurately on the surface of the Earth (or map sheet), topographic maps have two kinds of referencing systems:
• universal transverse mercator (UTM) projection (easting/northing)
• universal transverse mercator (UTM) projection (easting/northing)
• geographic: degrees and minutes (longitude/latitude)
The projection used for topographic maps is UTM. The UTM grid is a square grid system of lines depicted on maps and based on the transverse mercator projection. It can be used to accurately locate the position of features on the map by distance or direction. To express your location in grid coordinates or geographic coordinates, read the following section.
To find or express a location on a Topographic map :
One can find or express a location on a map by using geographic coordinates (longitude, latitude) or by using UTM grid coordinates (easting, northing).
Geographic coordinates are expressed in degrees,
Geographic coordinates are expressed in degrees,
minutes and seconds and can be determined on the map by using the longitude and latitude graticules
placed along the edges of the map. Latitude graticules are placed along the east and west edges of the map and longitude graticules are placed along the north and south edges of the map. The longitude
and latitude of your location can be determined by projecting your location to the map edges and then
by reading the corresponding latitude and longitude values.
 UTM grid coordinates are expressed in metres and can be determined on the map by using the UTM grid lines. These grid lines are equally spaced horizontal and vertical lines superimposed over the entire map. The coordinate value for each grid line can be found along the edge of the map. Northing values can be read along the east or west edges of the map and easting values can be read along the north or south edges of the map. The easting and northing of your location can be determined by projecting your location to the nearest horizontal and vertical grid lines and then reading the corresponding easting and northing values.
UTM grid coordinates are expressed in metres and can be determined on the map by using the UTM grid lines. These grid lines are equally spaced horizontal and vertical lines superimposed over the entire map. The coordinate value for each grid line can be found along the edge of the map. Northing values can be read along the east or west edges of the map and easting values can be read along the north or south edges of the map. The easting and northing of your location can be determined by projecting your location to the nearest horizontal and vertical grid lines and then reading the corresponding easting and northing values.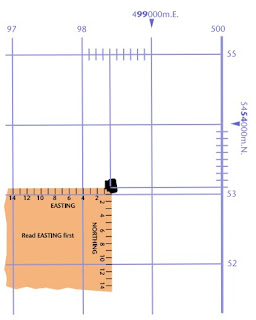
As an example, the position of the sportsplex located in the top right corner of 92-G/3 Lulu Island of British Columbia is located in UTM Zone 10 and the coordinates are 498400m.E. and 5453100m.N. The same position can also be described using geographic coordinates 123°01'E longitude, 49°14'N latitude.
To find a grid reference:
To find the map reference of a feature located at 984531 on a 1:50 000 scale topographic map,
Determine the easting:
• Read the grid line value left of the feature: 98.
• Read the grid line value left of the feature: 98.
• Estimate tenths of a square to the right (eastward) to feature: 4. Your easting is 984.
Determine the northing:
• Read the grid line value below the feature: 53.
• Estimate tenths of a square up (northward) to the feature: 1. Your northing is 531.
• The map reference for this feature is 984531.
Determine the northing:
• Read the grid line value below the feature: 53.
• Estimate tenths of a square up (northward) to the feature: 1. Your northing is 531.
• The map reference for this feature is 984531.
To navigate with a compass and a topographic map:
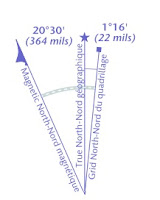 Navigating by compass requires determining bearings with respect to true or grid north from a map sheet and converting them to magnetic bearings for use with a compass.
Navigating by compass requires determining bearings with respect to true or grid north from a map sheet and converting them to magnetic bearings for use with a compass.
One way of doing this is described in the following steps:
1- Place the compass on the map with the direction-of-travel arrow pointing along the desired line of travel.
2- Rotate the compass dial so that the parallel lines within the capsule line up with the grid lines on the map. Convert the grid bearing to a magnetic bearing by using the information given (as in the accompanying diagram) on the map sheet. If declination is west, add it to the grid bearing; if declination is east, subtract it from the grid bearing.
Topographic Terminology
Bearing: The horizontal angle at a given point, measured clockwise from magnetic north or true
north to a second point.
Classified roads: Roads for which surface type, width and use are identified.
Contour lines: Lines on a map connecting points of equal elevation above mean sea level; using
contour lines, relief features can be profiled into a three-dimensional perspective.
Elevation: Vertical distance from a datum (usually mean sea level) to a point or object on the Earth’s surface.
Horizontal datum: The positional reference or basis for the geographic location of features on a map.
Legend: A description, explanation table of symbols, or other information, on a map or chart to provide a better understanding and interpretation of it.
Magnetic north: Direction to which a compass needle points.
Mean sea level: The average height of the surface of the sea for all stages of tide, used as a reference surface from which elevations are measured.
National Topographic System: An orderly index system suitable for a series of maps of different
scales for the coverage of Canada.
Projection: Geometric representation of the curved surface of the Earth on a flat sheet of paper.
Relief: The physical configuration of the Earth’s surface, depicted on a topographic map by contour lines and spot heights.
Spot elevation: A point on a map where height above mean sea level is noted, usually by a dot and elevation value; it is shown wherever practical (road intersections, summits, lakes, large flat areas and depressions).
Symbols: A diagram, design, letter or abbreviations, placed on maps, that (by convention, usage or reference to a legend) is understood to stand for or represent a specific feature or object.
Topography: Surface features both natural and man-made, collectively depicted on topographic
maps.
Unclassified roads: Roads for which the surface is unidentified.
Source : www.nrcan.gc

0 comments:
Post a Comment